HStoreField¶
Basic Usage¶
To use the HStoreField:
from django.db import models
from django_postgres_extensions.models.fields import HStoreField
class Product(models.Model):
description = HStoreField(null=True, blank=True)
The customized Postgres HStoreField adds the following features:
Individual keys¶
Get hstore values by key:
from django_postgres_extensions.models.expressions import Key, Keys obj = Product.objects.annotate(Key('description', 'Release')).get() obj = Product.objects.annotate(Keys('description', ['Industry', 'Release'])).get()
Update hstore by specific keys, leaving any others untouched:
Product.objects.update(description__ = {'Genre': 'Heavy Metal', 'Popularity': 'Very Popular'})
Database functions¶
Various database functions are included for interacting with HStores.
- Slice: Return a dictionary with just the specified keys
- Delete: Delete a key or list of keys from the hstore. Keys can also be deleted by specifying a dictionary
- AKeys: Returns the hstore keys as a list
- AVals: Returns the hstore values as a list
- HStoreToArray: Returns the hstore as an array
- HStoreToMatrix: Returns the hstore as a matrix
- HstoreToJSONB: Returns the hstore as JSON, with values adapated to their correct Python data types (hstore normally only returns values as strings)
- HstoreToJSONBLoose: Same as HstoreToJSONB, but attempt to distinguish numerical and Boolean values so they are unquoted in the JSON
For more information on these functions, check the postgresql documentation for each one. These functions handle the arguments by converting them to the correct expressions automatically:
from django_postgres_extensions.models.functions import *
obj = Product.objects.queryset.annotate(description_slice=Slice('description', ['Industry', 'Release'])).get()
obj = Product.objects.update(description = Delete('description', 'Genre'))
obj = Product.objects.update(description = Delete('description', ['Industry', 'Genre']))
Product.objects.update(description=Delete('description', {'Industry': 'Music', 'Release': 'Song', 'Genre': 'Rock'}))
Product.objects.annotate(description_keys=AKeys('description')).get()
Product.objects.annotate(description_values=AVals('description')).get()
Product.objects.annotate(description_array=HStoreToArray('description')).get()
Product.objects.annotate(description_matrix=HStoreToMatrix('description')).get()
Product.objects.annotate(description_jsonb=HstoreToJSONB('description')).get()
Product.objects.annotate(description_jsonb=HstoreToJSONBLoose('description')).get()
Use With Nested Form Field¶
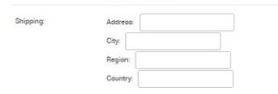
django.contrib.postgres includes a HStoreField for forms where you have to enter a hstore value programatically. Django Postgres Extensions adds a NestedFormField and NestedFormWidget (subclassed from the Django MultiValue Field and Widget) for use with a HStore Field. To use it specify a list of fields or a list of keys as a keyword argument to the Hstore Model field, but not both:
class Product(models.Model):
shipping = HStoreField(keys=('Address', 'City', 'Region', 'Country'), blank=True, default={})
The field would look like: